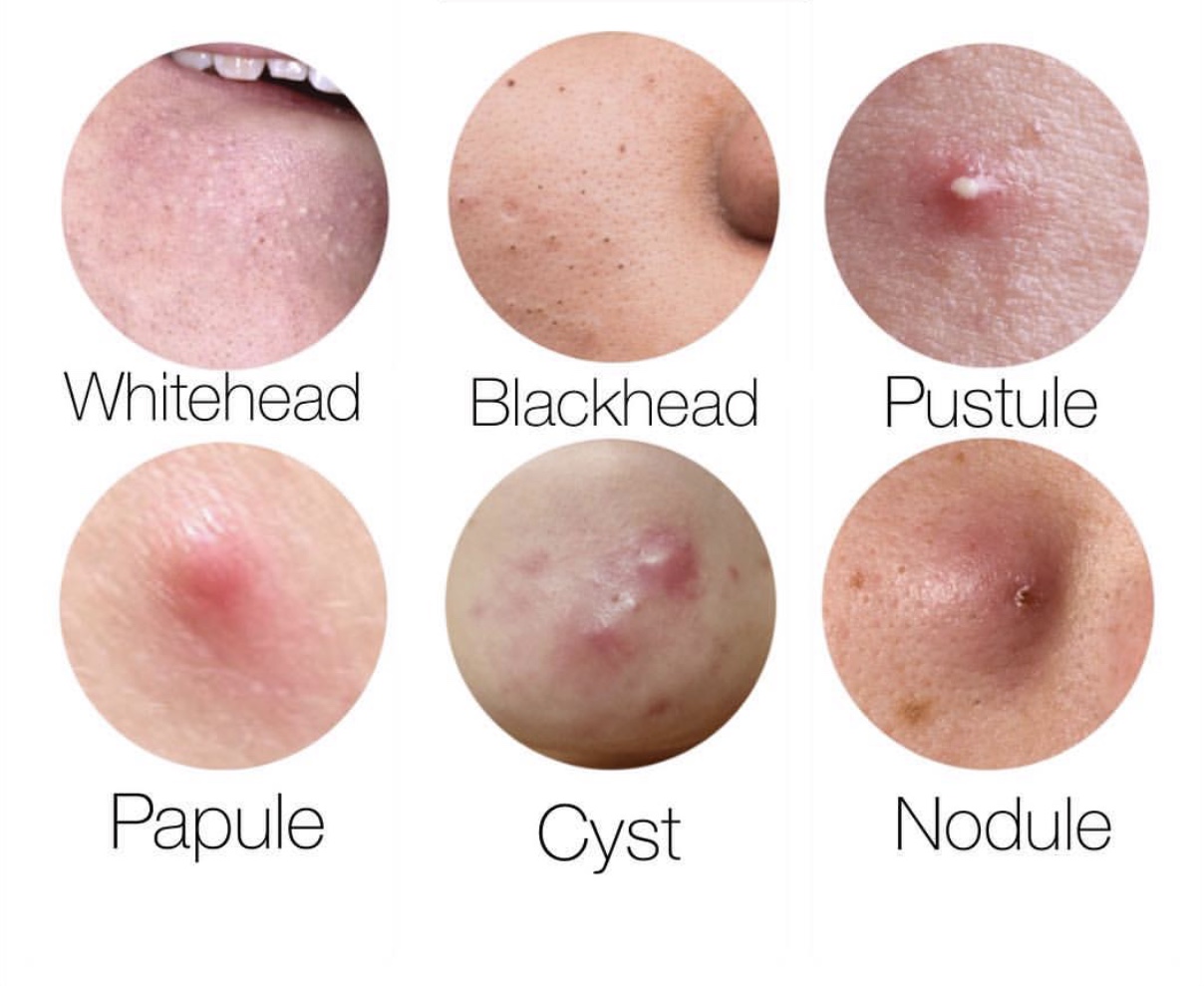
What Type of Acne Do You Have?
Acne is the most common chronic skin condition of the sebaceous glands. Half the time when you notice something sprout on our face, it’s hard to distinguish why or how it got there. All you’re probably thinking is HOW CAN I GET RID OF THIS PLANET ON MY FACE! Now, to understand how it should be treated, it’s important to first identify what type you have.
WHITEHEADS (Closed Comedones): Hardened sebum (oil) and skin cells in the follicle. Whitehead (Closed Comedo) These are not open to the air or oxygen. They are trapped by dead skin cells and need to be exfoliated or extracted.
BLACKHEADS (Open Comedones): The pore is open at the surface and exposed to air caused by a buildup of debris, oil, and dead skin cells in the follicles. The reason for the darkening of the sebum (oil) is because oxidation occurs.
PAPULE: Is a closed comedo without a "whitehead". Instead of becoming a blackhead, it becomes large enough to break the follicle sac. Once this happens, the immune system sends white blood cells to the area, depositing digestive enzymes to dissolve the impaction. Inflammation occurs and a painful, elevated, red lesion that doesn't form any pus.
PUSTULE: When a papule is not dissolved by enzymes, white blood cells continue to engulf the follicle wall, forming pus. As the pus builds up, white blood cells migrate to the surface, bringing impacted material with them and dilating the opening to for ma pustule. Pustule formation elevates pressure on the nerve ending and pain is subdued.
CYST: When there is intense inflammation in a follicle, thousands of white blood cells invade the site and create a large, soft, pus-filled lesion resembling a boil. Any lesion larger than one centimeter is considered a cyst. This acne is mostly hormone-induced and can remain on the skin for weeks or months. The depth and inflammation associated with cystic acne can destroy the follicle ,resulting in scarring.
NODULE: When the break in the follicle is near the bottom, a nodule forms. It's a sore, red lesion that is larger, deeper, and firmer than a papule. They are smaller bumps caused by conditions such as scar tissue, fatty deposits, or infections